INDIAN ARMED FORCES CHIEFS ON OUR RELENTLESS AND FOCUSED PUBLISHING EFFORTS

The insightful articles, inspiring narrations and analytical perspectives presented by the Editorial Team, establish an alluring connect with the reader. My compliments and best wishes to SP Guide Publications.

"Over the past 60 years, the growth of SP Guide Publications has mirrored the rising stature of Indian Navy. Its well-researched and informative magazines on Defence and Aerospace sector have served to shape an educated opinion of our military personnel, policy makers and the public alike. I wish SP's Publication team continued success, fair winds and following seas in all future endeavour!"

Since, its inception in 1964, SP Guide Publications has consistently demonstrated commitment to high-quality journalism in the aerospace and defence sectors, earning a well-deserved reputation as Asia's largest media house in this domain. I wish SP Guide Publications continued success in its pursuit of excellence.
- Operation Sindoor: Resolute yet Restrained
- India’s Operation Sindoor Sends a Clear Message to Terror and the World – ‘ZERO TOLERANCE’
- Japan and India set forth a defence cooperation consultancy framework, talks on tank and jet engines
- Terrorist Attack in Pahalgam in Kashmir: Unfolding a long surgical war against PAK
- Lt General Pratik Sharma takes over Command of Indian Army's Northern Command
Multi-Utility UGV & Scalable AIP
India's advances in indigenous military innovation underscore enhanced combat capability, operational endurance, and progress under 'Atmanirbhar Bharat'
 |
The Author is Former Director General of Information Systems and A Special Forces Veteran, Indian Army |

On December 5, 2025, Indian Army unveiled the nation's first indigenously developed multi-utility Unmanned Ground Vehicle (UGV), the cutting-edge platform named 'Sapper Scout RP Ver 2.0'. This multi-utility UGV made its public debut at 'Inno-Yoddha 2025', the Indian Army's annual innovation showcase held at the Manekshaw Centre at New Delhi. Major Rajprasad RS of 7 Engineer Regiment showed the 'Sapper Scout RP Ver 2.0' to Indian Army Chief General Upendra Dwivedi. Significantly, this innovation is Major Rajprasad's 12th innovation, reflecting a prolific track record, with four of his earlier systems already inducted into active Army operations over the past two years.
Built in-house to operate in demanding combat environments, the Sapper Scout RP Ver 2.0 brings together a suite of mission capabilities in a single platform that includes: mine detection; reconnaissance and surveillance; payload and logistics carriage; vehicle-based mine scattering; casualty evacuation, weapon, counter-UAS and sensor integration. Sapper Scout RP Ver 2.0 features a six-wheel independent drive, articulated suspension, and high mobility across rugged terrain. Equipped with advanced obstacle detection and environmental detection sensor systems, it can reconfigure rapidly because of its modular structure.
Indian Army unveiled the nation's first indigenously developed multi-utility Unmanned Ground Vehicle (UGV), the cutting-edge platform named 'Sapper Scout RP Ver 2.0'
With the next-era battlefield demanding rapid integration of manned and unmanned platforms, this UGV enhances the Army's Manned-Unmanned Teaming (MUM-T) capabilities and supports multi-domain operations. Sapper Scout RP Ver 2.0 is being viewed as a force multiplier for infantry, mechanised units, and engineer formations, with key operational advantages that include: remote engagement in hostile zones; reconnaissance in high-risk and confined areas; ammunition, fuel, and supplies movement; flank protection for advancing troops; deployment of counter-UAS grids; support in deserts, plains and high-altitude terrain.
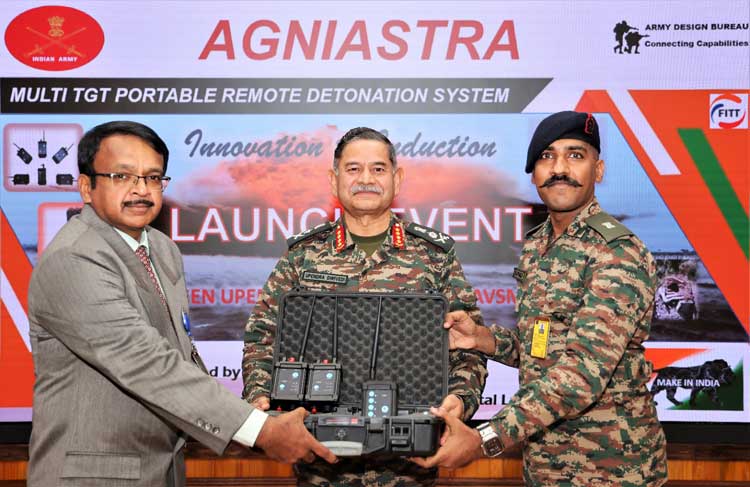

Major Rajprasad's previous innovations, including 'Vidyut Rakshak', an IoT-based generator monitoring system, and 'AgniAstra', a portable multi-target detonating device, are already in service. Sapper Scout RP Ver 2.0 would strengthen India's growing ecosystem of indigenous military robotics and battlefield innovation. With the Army actively accelerating innovations under its Atmanirbhar Bharat framework, Sapper Scout RP Ver 2.0 is expected to progress towards formal evaluation and eventual induction into operational units.
With the next-era battlefield demanding rapid integration of manned and unmanned platforms, this UGV enhances the Army's Manned-Unmanned Teaming (MUM-T) capabilities and supports multi-domain operations
Concurrently, the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has reaffirmed its confidence in the scalability of its indigenous Air-Independent Propulsion (AIP) technology, confirming its readiness to power the Indian Navy's next-generation Project–76 (P-76) submarines. The DRDO had originally designed the AIP system for the compact Kalvari-class (Scorpene) submarines. However, DRDO officials confirm that this fuel-cell based system is fully adaptable for larger platforms, promising enhanced stealth and endurance for the Indian Navy's future underwater combatants.
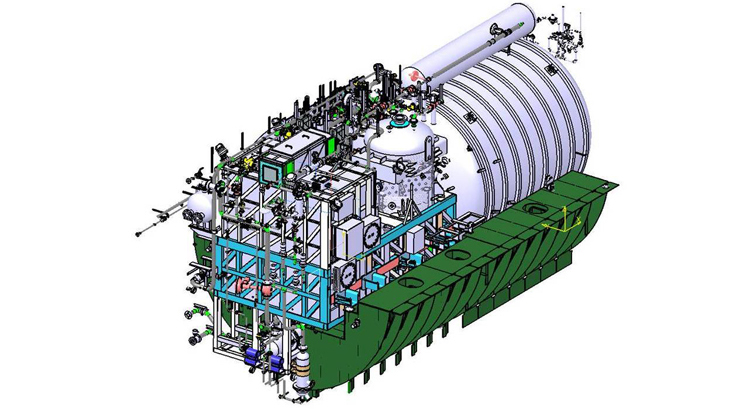
According to recent internal reviews, the AIP system features a modular architecture, with the design allowing the fuel-cell stacks to be configured in parallel to meet higher power generation requirements. The technology being highly scalable, a DRDO official has said, "By increasing the number of fuel-cell stacks and refining the thermal management system, we can seamlessly adapt the propulsion to meet the rigorous demands of the Navy's blue-water operations."
DRDO has reaffirmed its confidence in the scalability of its indigenous Air-Independent Propulsion (AIP) technology, confirming its readiness to power the Indian Navy's next-generation Project–76 (P-76) submarines
Project 76 aims to provide a quantum leap in Indian Navy's operational capabilities; also representing a massive stride towards self-reliance (Atmanirbhar Bharat) in maritime defence. Envisioned as a fully indigenous conventional submarine programme with an estimated budget of ₹12 lakh crore, these submarines will significantly outperform their predecessors. Unlike the compact Kalvari-class, the P-76 submarines are expected to have a displacement of 3,000-4,000 tonnes. This is a 40 per cent increase in size is designed to accommodate: Advanced Vertical Launch System (VLS) capable of firing BrahMos supersonic cruise missiles; Extended Crew Endurance for long range deployments in the Indo-Pacific; High-Performance Sensor Suites and electronic warfare (EW) systems. To sustain these energy-intensive system, the upscaled AIP configuration is projected to deliver outputs exceeding 200 kW, doubling the capacity of the current 100-120 kW modules designed for the Kalvari-class.
The integration of AIP is a game-changer for conventional diesel-electric submarines, allowing them to recharge their batteries without surfacing for atmospheric oxygen, a vulnerability that often exposes submarines to enemy radar. With the enhanced AIP systems, P-76 submarines are targeted to achieve submerged endurance of four to five weeks at low speeds. This capability is critical for shadowing operations in strategic choke points like the Malacca Straits and the Arabian Sea. The technology has already undergone rigorous validation, with land-based prototypes demonstrating reliability and a module slated for integration into INS 'Kalvari' during the upcoming refit expected in 2025-2026.
The integration of AIP is a game-changer for conventional diesel-electric submarines, allowing them to recharge their batteries without surfacing for atmospheric oxygen, a vulnerability that often exposes submarines to enemy radar
A key tenet of Project-76 is its high-level of indigenisation. The DRDO is collaborating closely with Indian industry majors, including Larsen and Toubro (L&T) and tata to scale the production of AIP components. This partnership aims to achieve up to 90 per cent local content by the time the submarines are inducted, drastically reducing lifecycle costs and dependence on foreign OEMs. This development comes at a time when the Indian Ocean region (IOR) is witnessing increased underwater activity, notably from the proliferation of China's Type 039A Yuan-class AIP submarines and the supply of Hangor-class submarines to Pakistan. Project-76, together with India's nuclear-powered submarines (SSBNs), serve as a vital component in countering emerging threats and to fortify our maritime borders.





